Mastering carbon sequestration farming requires more than just following basic instructions—it demands a deep understanding of the underlying principles and the ability to adapt techniques to unique situations and challenges.
This expert-level guide is designed for serious homesteaders who want to push the boundaries of what’s possible with carbon sequestration farming. We’ll explore cutting-edge approaches, dive into the latest research, and share insights from leading practitioners in the field.
This comprehensive resource covers:
- Advanced theoretical frameworks for carbon sequestration farming
- Innovative techniques and emerging best practices
- Complex system integration strategies
- Troubleshooting advanced challenges
- Research-backed optimization methods
The Science Behind Carbon Sequestration Farming
Carbon Sequestration Farming represents a paradigm shift from conventional agriculture to practices that actively restore and enhance ecosystem health. Unlike sustainable farming, which aims to maintain current conditions, regenerative practices actually improve soil health, increase biodiversity, and sequester carbon over time.
Core Principles of Regenerative Agriculture
1. Minimize Soil Disturbance
Healthy soil is a complex ecosystem of billions of microorganisms. Excessive tillage destroys this delicate web of life:
- Implement no-till or minimal-till practices
- Use cover crops to protect soil surface
- Employ broad-fork tools for gentle soil decompaction
- Allow natural soil aggregation to develop
2. Maximize Crop Diversity
Monocultures are vulnerable to pests, diseases, and market fluctuations. Diversity creates resilience:
- Rotate crops to break pest and disease cycles
- Integrate perennial crops with annuals
- Use companion planting strategies
- Include nitrogen-fixing plants in rotations
3. Keep Living Roots in Soil Year-Round
Living roots feed soil microorganisms and prevent erosion:
- Plant cover crops between cash crops
- Use perennial pastures and hay crops
- Implement relay cropping techniques
- Maintain ground cover through mulching
4. Integrate Livestock Thoughtfully
Animals can be powerful tools for land regeneration when managed properly:
- Use rotational grazing to mimic natural herd movements
- Allow adequate rest periods for pasture recovery
- Match animal species to landscape and goals
- Integrate animals with crop production systems
Implementing Carbon Sequestration Farming on Your Homestead
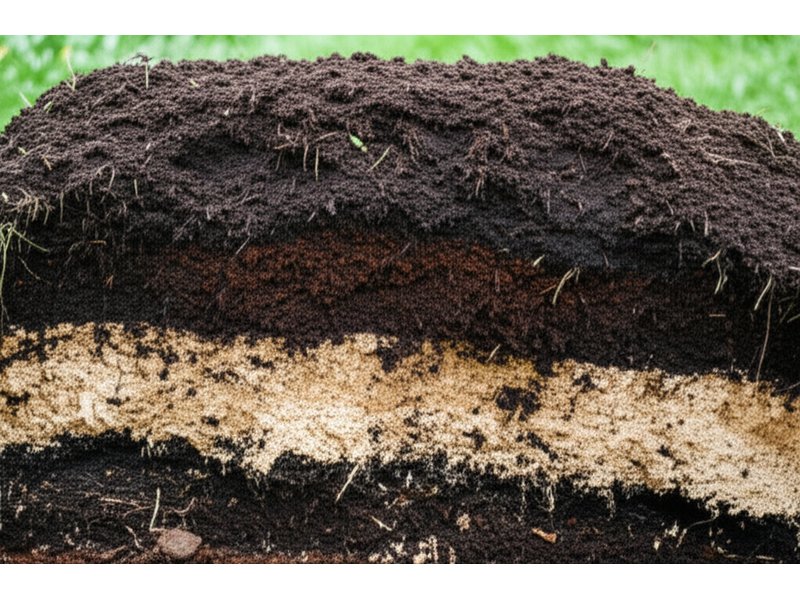
Soil Health Assessment and Improvement
Testing Beyond NPK
Standard soil tests only tell part of the story. For regenerative farming, also assess:
- Organic matter percentage (aim for 4-6%)
- Soil biology activity levels
- Water infiltration rates
- Aggregate stability
- Microbial diversity
Building Soil Biology
Healthy soil contains billions of beneficial microorganisms:
- Add compost and compost teas regularly
- Minimize chemical inputs that harm soil life
- Use mycorrhizal inoculants when establishing new plantings
- Feed soil organisms with diverse organic matter
Cover Cropping Strategies
Selecting Cover Crop Mixes
Different cover crops provide different benefits:
- Legumes (clover, vetch) fix nitrogen
- Grasses (rye, oats) build soil structure
- Brassicas (radishes, turnips) break compaction
- Mix species for maximum benefit
Timing and Management
- Plant cover crops immediately after harvest
- Allow adequate growth before termination
- Use crimping or mowing instead of tillage
- Plan termination timing for cash crop planting
Water Cycle Restoration
Increasing Water Infiltration
Healthy soil can absorb and hold more water:
- Build organic matter to increase water-holding capacity
- Create swales and berms to capture runoff
- Use mulch to reduce evaporation
- Implement keyline design principles
Reducing Erosion
Protect your valuable topsoil:
- Maintain ground cover year-round
- Plant perennial strips on slopes
- Use contour farming techniques
- Install appropriate drainage systems

>
Advanced Regenerative Techniques
Carbon Sequestration Strategies
Maximizing Carbon Storage
Your farm can become a carbon sink:
- Increase perennial plantings
- Build soil organic matter through composting
- Use biochar as a soil amendment
- Implement silvopasture systems
Measuring Carbon Impact
Track your progress:
- Monitor soil organic matter changes
- Calculate carbon footprint reductions
- Document biodiversity improvements
- Measure water infiltration improvements
Integrated Pest Management
Building Natural Pest Control
Healthy ecosystems regulate themselves:
- Encourage beneficial insects with diverse plantings
- Use trap crops to protect main crops
- Implement push-pull strategies
- Maintain habitat for natural predators
Reducing Chemical Inputs
Gradually reduce reliance on external inputs:
- Build soil health to reduce fertilizer needs
- Use biological pest control methods
- Implement crop rotations to break pest cycles
- Focus on prevention rather than treatment
[IMAGE_PLACEHOLDER_1]
Economic Benefits of Carbon Sequestration Farming
Cost Savings Over Time
- Reduced input costs (fertilizers, pesticides)
- Lower fuel costs from reduced tillage
- Decreased irrigation needs
- Improved crop resilience and yields
New Revenue Opportunities
- Premium prices for regeneratively grown products
- Carbon credit programs
- Agritourism and educational workshops
- Value-added product development
Risk Reduction
- Greater resilience to weather extremes
- Reduced dependence on external inputs
- Diversified income streams
- Improved long-term land productivity
[IMAGE_PLACEHOLDER_2]
Measuring Success in Regenerative Farming
Key Performance Indicators
- Soil organic matter percentage
- Water infiltration rates
- Biodiversity indices
- Carbon sequestration rates
- Economic profitability
Long-term Monitoring
- Annual soil tests
- Photographic documentation
- Yield and quality records
- Financial performance tracking
- Ecosystem health assessments
The transition to carbon sequestration farming takes time and patience, but the long-term benefits for your land, your family, and the planet make it one of the most important investments you can make in your homestead’s future.
Taking Action with Carbon Sequestration Farming
Mastering carbon sequestration farming is a journey that requires patience, practice, and persistence. The techniques and strategies outlined in this guide provide a solid foundation for success, but remember that every homestead is unique. Adapt these methods to your specific situation, climate, and goals.
Start with one or two techniques that resonate most with you, and gradually expand your skills as you gain confidence and experience. Don’t be discouraged by initial setbacks—they’re part of the learning process and often lead to the most valuable insights.
The homesteading community is incredibly supportive and generous with knowledge sharing. Connect with local homesteaders, join online forums, and don’t hesitate to ask questions. Your success contributes to the broader movement toward sustainable, self-sufficient living.
—
Related Articles:
- [Essential Homesteading Skills](https://homesteadingalliance.com/essential-homesteading-skills/)
- [Beginner Homesteading Projects](https://homesteadingalliance.com/beginner-homesteading-projects/)
- [Homesteading For Beginners](https://homesteadingalliance.com/homesteading-for-beginners/)
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you. Read our full disclosure policy.